 Of the over 2 million rear-end accidents in the United States every year, a significant number of folks end up experiencing chronic pain and impairment. Some studies have shown that 1 out of 5 people are still in pain 12 months after a collision.
Of the over 2 million rear-end accidents in the United States every year, a significant number of folks end up experiencing chronic pain and impairment. Some studies have shown that 1 out of 5 people are still in pain 12 months after a collision.
Dr. Weinberg sees many accident cases in our Smyrna, GA location, and we oftentimes see patients who have been suffering for many years and have not been able to find relief. Dr. Weinberg has great success in treating these patients.
What Causes Chronic Pain after a Crash?
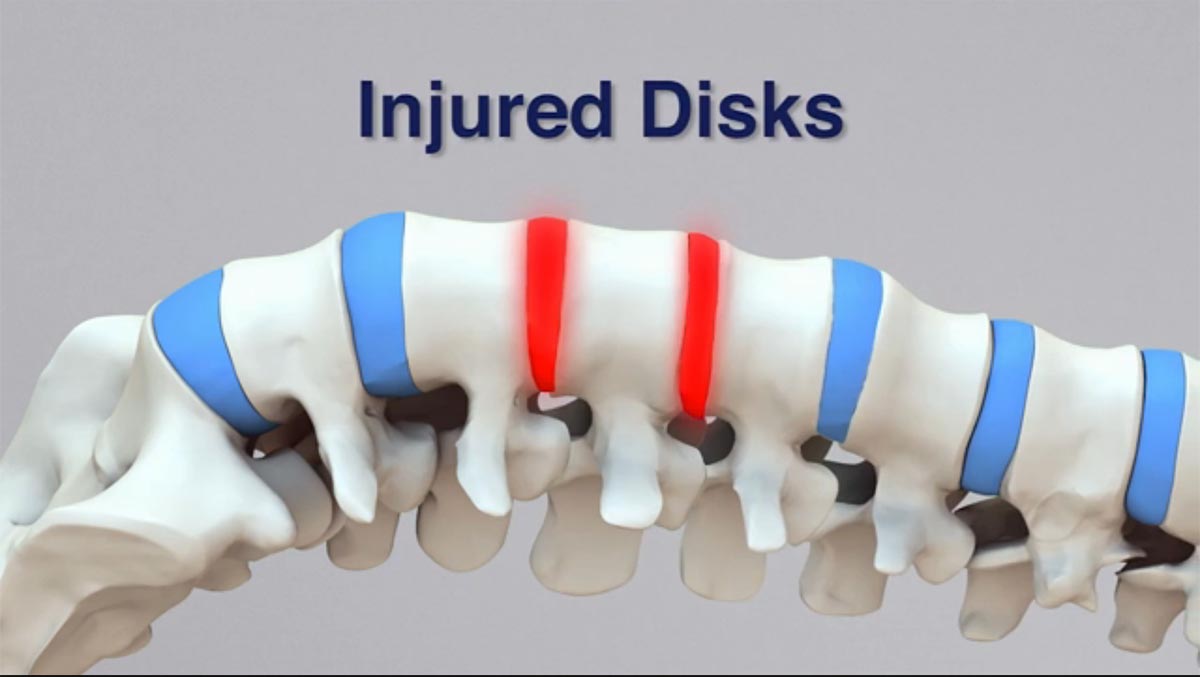
During a crash, the structures of your spine can be sprained or torn. The damaged area becomes swollen and irritated and transmits pain signals to the spine and brain.
Pain tells your nervous system that something is wrong, which tells the muscle tissues in the damaged area to contract to shield the area from further injury.
If the injury isn't addressed immediately, a negative cycle develops. The damaged area keeps sending pain signals and each time, your nervous system reacts. This brings about a feedback loop in your nervous system that researchers refer to as "central sensitization." Your nervous system essentially becomes oversensitive to any kind of stimulus, producing chronic pain.
Dr. Weinberg is able to help this kind of problem, as chiropractic care is a proven way to restore the nervous system's healthy functioning. Studies show that chiropractic is effective at relieving pain from car crashes and shows that chiropractic in fact has positive effects on the pain centers of the brain.
If you live in Smyrna, GA and have been in a crash, you don't have to suffer with chronic pain. Give Dr. Weinberg a call today at (678) 214-4445 for a consultation or appointment.
- Ferrari R. A prospective study of the 1-year incidence of fibromyalgia after acute whiplash injury. Rheumatic & Musculoskeletal Disease 2015; doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2014-000007.
- Stone AM, Vicenzino B, Lim EC, Sterling M. Measures of central hyperexcitability in chronic whiplash associated disorder - A systematic review and meta-analysis. Manual Therapy 2012;18(2):111-7.
Remond Weinberg